MIPI Made Simple: Quick Start Guide with Expert’s Tips
Introduction to MIPI
Welcome to our Quick Start Guide series! In this first installment, we’re diving into the world of MIPI, or Mobile Industry Processor Interface. This high-speed interface is a key player in the technology landscape, particularly in mobile devices and other small devices. But what exactly is MIPI, and why is it important? Let’s find out.
In the following parts of this series, we will also explore other key interface technologies such as eDP and LVDS. Stay tuned to learn more about these important technologies.
What is MIPI?
MIPI is a high-speed differential protocol that’s widely used in smartphones and increasingly popular in industrial PCs. The MIPI Display Serial Interface (DSI) technology was created specifically for display communication, making it a crucial component in delivering high-quality visuals on your device’s screen.
When and Where to Use MIPI?
MIPI is particularly suitable for mobile devices and other small devices due to its high-speed capabilities and low-power operation. It’s an excellent choice for applications that require fast data transmission, high-quality visuals, and energy efficiency. Whether you’re designing a smartphone, a smart gadget, or an industrial PC, MIPI can provide a powerful and efficient solution for display communication. As a general rule of thumb when selecting an interface for Industrial PCs (IPC), MIPI is generally suitable for small device screens when choosing display interface technologies.
Features and Benefits of MIPI
MIPI comes with a host of benefits that make it a top choice for display communication. Here are some key features:
- High-Speed Interface: MIPI can signal data quickly, exceeding minimum frame rate requirements. This makes it capable of handling a large amount of data and supporting high-speed applications such as video transmission.
- Low-Power Displays: A differential clock pair is part of the MIPI interface, which clocks both the signals and the data lines at a high frequency. This results in low-power displays, making MIPI an energy-efficient choice.
- High-Quality Visuals: MIPI interface displays may be capable of supporting high resolution and rich color rendering, providing an excellent visual experience for users.
Practical Insights: Optimizing MIPI Interface for Noise Reduction
When it comes to implementing MIPI in your projects, there are a few practical tips to keep in mind:
- Cable Length: The ideal cable length for MIPI to minimize noise is 5 cm. Keeping the distance between the MIPI transmitter and the receiver as short as possible can help maintain signal integrity and reduce noise interference.
- Signal Degradation: As the length of a cable increases, the signal has to travel a longer distance. This can lead to signal degradation due to factors like resistance, capacitance, and inductance of the cable. The longer the cable, the more these factors can degrade the signal.
- Noise Interference: Longer cables also have a larger surface area that can pick up electromagnetic interference (EMI) from the environment. This can add noise to the signal, further degrading its quality.
- Signal Reflections: In high-speed data transmissions, signal reflections can become a significant issue with longer cables. These reflections occur when the signal encounters a change in impedance, such as at the connection between the cable and the receiver. The reflections can travel back along the cable and interfere with subsequent signals.
- Cable Type: Using Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) is better than Flat Flexible Cable (FFC) for MIPI interfaces.
- Signal Integrity: FPCs are designed with controlled impedance, which can be crucial for high-speed data transmission like MIPI. This ensures that the signal integrity is maintained over the length of the cable, reducing the likelihood of data loss or corruption.
- Flexibility and Durability: FPCs are more flexible and durable than FFCs. They can be bent and folded without damaging the circuits, making them ideal for applications where space is limited or where the cable needs to be routed around corners or other obstacles.
- Customization: FPCs can be custom designed to fit specific applications, including the placement of components, the number of layers, and the routing of signals. This allows for more efficient use of space and can improve the overall performance of the interface.
- Reduced Crosstalk and Interference: The design of FPCs can help to reduce crosstalk and electromagnetic interference (EMI), both of which can degrade signal quality in high-speed data transmission.
- Reliability: FPCs are generally more reliable than FFCs, especially in harsh environments or in applications where the cable may be subject to repeated flexing.
- Circuit Wiring: When using FPC, ensure each signal circuit wire is evenly located on the cable. For power circuits, it’s okay if they’re not evenly located.
- Signal Integrity: In high-speed data transmission like MIPI, the signal quality is crucial. If the signal circuit wires are not evenly located on the cable, it can lead to signal degradation due to impedance mismatches. Impedance mismatch can cause signal reflections, which can degrade the signal quality and lead to data errors.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): When signal circuit wires are evenly located on the cable, it can help to reduce electromagnetic interference. EMI can cause noise in the signal, which can degrade the signal quality and lead to data errors.
- As for power circuits, they are less sensitive to these issues. The current in power circuits is typically steady (DC or low frequency), so they are less susceptible to impedance mismatch issues and EMI. Therefore, it’s okay if power circuits are not evenly located on the cable.
- Circuit Direction: Maintaining the straightness of signal circuits in a cable is crucial for preserving signal integrity in high-speed data transmissions like MIPI. When the signal path changes direction abruptly, it can lead to signal reflections and loss due to impedance mismatches. Moreover, such changes can increase the risk of crosstalk, where a signal in one circuit interferes with a signal in a nearby circuit. Therefore, it’s recommended to keep the signal circuits as straight as possible. If turning is necessary, aim for an angle not greater than 90 degrees to minimize these potential issues.
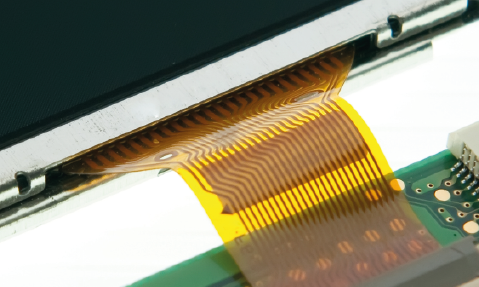
Ensure the turning angle of the signal circuits is less than 90 degrees.
Conclusion
MIPI is a powerful interface technology that’s shaping the future of display communication. By implementing the expert’s tips from this article, you can ensure that your MIPI signals will have less noise, leading to improved performance and reliability. With its high-speed capabilities, low-power operation, and high-quality visuals, it’s no wonder MIPI is becoming a popular choice in the tech industry, especially for mobile and small devices. Stay tuned for our next Quick Start Guide, where we’ll explore another key interface technology: eDP.
For more detailed information on how MIPI compares with other interface technologies like eDP and LVDS, check out our comprehansive comparison article – MIPI vs. eDP vs. LVDS.
Primax and LV-Tron Announce Strategic Partnership to Revolutionize Smart Meeting Solutions
Primax Electronics and LV-Tron (a division of IAdea) have officially announced their strategic partnership to invest in and develop cutting-edge smart meeting solutions. This collaboration aims to position both companies as leaders in the smart meeting industry, with...
Understanding SCEP: Its Role in Android Security
Understanding SCEP: Its Role in Android Security Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) plays a vital role in digital security. Within Android, SCEP has become an essential tool, simplifying the once complex process of certificate enrollment. This article...
802.1X over Ethernet: A Key Solution for a More Secure Network
802.1X over Ethernet: A Key Solution for a More Secure Network Introduction to 802.1X over Ethernet In an era where network security is paramount across various industries, understanding and implementing robust security measures is essential. Last time, we delved into...
IEEE 802.1X Explained: A Plainspeak Guide to Securing Your Network
IEEE 802.1X Explained: A Plainspeak Guide to Securing Your Network Introduction to 802.1X 802.1X (The "X" is typically capitalized) is a cornerstone of modern network security and one of the most widely adopted security measures today. Here's why: Popularity: 802.1X...
A Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding Hardened Android
A Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding Hardened Android Introduction to Hardened Android In the world of mobile operating systems, Android stands out for its open-source nature, which allows for extensive customization. However, this flexibility can sometimes lead to...
Revolutionizing Business Collaboration with LV-Tron’s Immersive Smart Conference Rooms
rRevolutionizing Business Collaboration with LV-Tron's Immersive Smart Conference Rooms Introduction: Unveiling the Power of Smart Conference Rooms In the dynamic landscape of the digital age, the traditional conference room has been transformed into a "smart...
Android vs Windows: A User’s Guide to Choosing the Right OS
Android vs Windows: A User's Guide to Choosing the Right OS Choosing the right operating system for industrial PCs is crucial. This article provides a comprehensive comparison between Android and Windows, focusing on CPU choices, memory usage, and storage usage....
Joint Development Manufacturing (JDM): The LV-Tron Advantage
Joint Development Manufacturing: The LV-Tron Advantage In the tech industry, Joint Development Manufacturing (JDM) is a game-changer. It offers numerous benefits such as cost savings, faster time to market, and access to specialized expertise. But at LV-Tron, we don't...
LVDS Made Simple: Quick Start Guide with Expert’s Tips
LVDS Made Simple: Quick Start Guide with Expert’s Tips Introduction to LVDS Welcome back to our Quick Start Guide series! We've previously explored the high-speed interfaces of MIPI and eDP, crucial in mobile devices and embedded systems respectively. Today, we’re...
eDP Made Simple: Quick Start Guide with Expert’s Tips
eDP Made Simple: Quick Start Guide with Expert’s Tips Introduction to eDP Welcome back to our Quick Start Guide series! In our previous installments, we delved into the world of MIPI, a high-speed interface crucial in mobile devices and small devices, and LVDS, ideal...
Conference Room Technology 2023: The Innovations You Can’t Ignore
Conference Room Technology 2023: The Innovations You Can't Ignore As we navigate the digital era, the landscape of conference room technology is evolving at an unprecedented pace. This rapid progression has ushered in a host of new software, integrations, and...
Overcoming Challenges in Shifting from Traditional to Hybrid Meetings
Overcoming Challenges in Shifting from Traditional to Hybrid Meetings The digital era has ushered in a new trend of hybrid meetings, which involve both internal employees and external teams from other companies. These meetings offer significant benefits, including...
Smart Meeting Room
The Essential Hardware for a Smart Meeting Room The Rising Trend of Smart Meetings: Embracing the Digital Era According to the 63rd International Meetings Statistics Report released by the Union of International Organizations (UIA) in 2022, the number of meetings is...
Understanding Android Industrial PCs: A Detailed Overview
Understanding Android Industrial Panel PCs: A Detailed Overview In the rapidly evolving world of industrial automation, Android Panel PCs have emerged as a game-changer. These powerful devices are transforming the way industries operate, offering unparalleled...
Comprehensive AIoT Industrial Computer Terminology Guide
Discover Optimized Solutions for Your Business Advantages. Contact Us Today!















